How is an organization's property tax calculated? What is property tax? How do general rules and regional specifics relate?
The easiest way to get an answer to the question of how to calculate an organization’s property tax in 2019 is to use an online calculator. It's easy to work with.
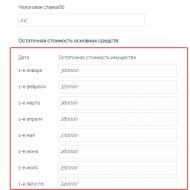
Step 1: Enter your tax rate. For budgetary organizations - 2%.
Step 2. Indicate in rubles the residual value of fixed assets at the beginning of each month and on the last day of the year. A separate field is provided for each digit. In total, you need to enter 13 values (two of them are December).

Step 3. When everything is ready, click on the Calculate button. The results will be displayed in the table below.

Features of taxation
The calculation of the property tax of organizations, as well as the general requirements for the specified obligation to pay tax, are defined in Chapter. 30 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The tax is recognized as regional, that is, the authority to determine the rates, terms and procedure for payment and additional benefits has been transferred to the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. Tax rates and the procedure for applying differentiating coefficients are approved by regional legislative acts.
Payers are legal entities that own (on balance, for temporary use) movable or immovable fixed assets that are recognized as an object of taxation. Budgetary institutions do not have preferential benefits. Lists of objects that are not subject to taxation and preferential categories of institutions are presented in detail in Art. 374 and 381 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Calculation of property tax for legal entities in 2019
This issue is regulated by clause 4 of Art. 376 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. To determine the tax base for an obligation regarding the organization’s property, the criteria of PBU 6/01 and the All-Russian Classifier of Fixed Assets (hereinafter referred to as OKOF) are used. Order of Rosstandart No. 458 dated April 21, 2016 regulates the transition of fixed assets to a new classifier. The document contains a detailed and clarified description of codes and decryptions.
Calculate property taxes in 2019 in a new way. Before drawing up a declaration or intermediate (advance) calculation, update the OKOF, and when calculating the tax base, exclude the objects that are listed in clause 4 of Art. 374 and art. 381 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, that is, those that are excluded from the base:
- fixed assets classified in the first or second group of the updated classifier;
- land objects and environmental management objects;
- movable fixed assets acquired after January 1, 2013 (except for property that was taken into account as a result of the reorganization or liquidation of legal entities, and property of interdependent persons, in accordance with the conditions of clause 2 of Article 105.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- Fund objects not accepted for balance, in accordance with accounting requirements.
State employees calculate and transfer taxes to the appropriate budget at the average annual cost. But there are exceptions! They are determined individually, so they are clarified only by the tax office.
Calculation examples
Let's look at several examples of calculating such taxes. We remind you that you can use the calculator for free on our website.
Let's calculate the amount of the annual payment to the regional budget using the linear depreciation method for public sector employees, assuming that the regional tax rate is 2%. Let's calculate the average annual cost using the formula:
Cryear = (C1 + C2 + C3... + C12 + C13) : (12 months + 1), where:
- C1-12 - monthly accounting data (as of January 1, February 1, and so on);
- C13 - residual value at the end of the reporting period (tax year).
Let's determine the amount of tax using the formula:
N (year) = Srgod × Reg.rate: 100%, where:
- N (year) - the amount of tax for the year;
- Srgod - average annual value of property;
- Reg.rate is the tax rate of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation (region).
Example 1. A secondary school owns a non-residential building. According to accounting data, the residual value on the first day of each month was:
At the end of the tax period (December 31), the residual value is 280,000 rubles. We calculate using the first formula:
Сryear = (400,000 + 390,000 + 380,000 + 370,000 + 360,000 + 350,000 + 340,000 + 330,000 + 320,000 + 310,000 + 300,000 + 290,000 + 280,000) : ( 12+1) = 340 000 rub.
We calculate the payment amount for the tax period:
N = (340,000 × 2%): 100% = 6800 rub.
Example 2. A car is listed on the balance sheet of the cultural department (operated by the previous legal entity for more than 1.5 years). The car was purchased in July 2014 during the reorganization of a legal entity, and the purchase price was RUB 1,200,000. Useful life - 60 months. According to accounting data as of 01/01/2017 - 480,000 rubles, the service life of the institution as of the same date is 30 months.
Movable property that was accepted as part of the reorganization or liquidation of a legal entity before 01/01/2013 is not included in the base for calculating the organization’s tax (clause 25 of Article 381 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When determining the class of a car, the engine size is taken into account, which does not apply to executive class vehicles (the engine size does not affect which class the car is assigned to - always class 5). To determine the service life of a used vehicle, the date of initial commissioning plays an important role. From the initial date of operation of the first owner, the period of further useful use (hereinafter referred to as SPI, term) is determined. According to OKOF conditions, cars belong to 3 depreciation groups:
- third group - SPI 3-5 years;
- fourth group - period 5-7 years;
- fifth group - period 7-10 years.
Yearly for the first quarter of 2019 = (480,000 + 456,000 + 432,000 + 408,000): (3+1) = 1,776,000: 4 = 444,000 rub.
N for the first quarter 2019 = 1/4 × (444,000 × 2%: 100%) = 0.25 x 8,880 = 2,220 rubles.
Example 3. In January 2019, two laptops were transferred to an autonomous institution, at a price of 65,000 and 30,000 rubles. According to the new classification of PF, laptops and personal computers are classified in the 2nd depreciation group, which means that these fixed assets are not included in the tax base.
Example 4. Xerox (3rd depreciation group - OKOF 330.28.23.22) on the balance sheet of a municipal hospital since January 2016. Initial cost 80,000 rubles. SPI - 60 months. It is not included in the calculation of the taxable base (clause 25 of Article 381 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), since it was accepted for accounting after 01/01/2013 and relates to movable property (Article 130 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Example 5. Large metal safe worth RUB 300,000. registered in February 2013. The fixed asset is movable, that is, it is easily dismantled, purchased after 01/01/2013, therefore it is not included in the base for calculating taxes of organizations.
How to calculate property tax based on cadastral value for public sector employees
Organizations that are financed by budgets of all levels must calculate tax liabilities at the average annual cost, unless otherwise provided by law. Regional authorities have the right to establish a list of property that is subject to payment at cadastral value. On the first day of the reporting period (January 1), information is published on the official websites of the legislative body of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
If it is on the list, the accountant must:
- Request the cadastral value of real estate from Rosreestr.
- Calculate the share of the building in proportion to the occupied space if the property is in joint (shared) ownership.
- Calculate the size of the organization's tax liability based on the cadastral value for the year or quarter, if advance transfers are provided in your region.
Formula for calculations:
Tax liability of an organization's property at cadastral value (CVA) = cadastral value × tax rate × number of months of property ownership / number of months in the reporting period.
The amount of the advance transfer is equal to one-fourth of the annual property tax.
If the property is not on the approved list, continue to calculate your tax liability as before. If the list is missing or controversial issues arise, sign up for a consultation with the Federal Tax Service. There you can also clarify the details for transferring payments to the regional budget.
07.11.16 11 574 0
Who pays property taxes and when?
What is property tax
Property tax is a payment to the state for the ownership of real estate. You bought an apartment, registered it in your name - now you are the owner and you have real estate. You have to pay for the right to own it. More properties mean more tax liabilities.
Real estate tax is assessed once a year by the Federal Tax Service: in the second half of the year, it charges fees for properties that you owned in the previous reporting period. The Federal Tax Service generates a tax notice - a receipt - indicating what and how much to pay, and sends it to the owner. We have already written,
If you have a personal account on the tax website, by default you will not receive any notifications by mail. In order for them to arrive by mail, you need a paper delivery application. After registering in your personal account, you can choose whether to continue receiving paper receipts for debt by mail or refuse.
Who pays personal property tax
Property taxes are paid by property owners. It doesn’t matter who lives and is registered in the apartment: the taxpayer will be the one who owns it.
Objects of taxation
Only real estate is subject to tax. Which objects are movable and which are immovable is determined by Art. 130 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. For example, a car is considered a movable object, while a house, garage, or room in a communal apartment are considered immovable.
Movable property
The law defines movable property in the opposite way: these are any things that are not real estate. For example, a car, money, a TV or a Persian cat. The list of real estate is given in the civil code - property tax is not paid for property not listed in this list.
The law requires registration of rights to any real estate, but there is no such requirement for movable objects. Do not confuse it with the registration of vehicles in the traffic police: when issuing a vehicle passport, the car is registered, and the ownership of it is not registered. Due to the title, the owner is “tied” to the car, but this is not an analogue of ownership.
Vehicle owners do not pay property tax, but must pay vehicle tax to the government.
Real estate
There is no definition of real estate in the law - it simply provides a complete list of objects that are recognized as such. Not all real estate is subject to property tax. The list of what to pay for is also given in the law: residential building, apartment, room, garage or parking space. There are other, more rare objects of taxation.
Taxes on common property in apartment buildings are not paid.
Property tax rates for individuals
The rate is used to calculate the amount of property tax. The tax rate is a percentage of the tax base. And the tax base is the value of the object of taxation. For the calculation, they do not take the entire cost - and not the one indicated in the sales contract. The cost of an object is determined by government agencies, and there are two types: inventory or cadastral. But it is not necessary to understand the types of costs and deductions: all the data is indicated in the tax notice. The main thing is to check them before paying.
The law sets basic tax rates for individuals. They depend on the type of object and its value. If it is a residential building, apartment, room or garage - 0.1% of the cost, everything else - 0.5%, but for objects more expensive than 300 million rubles - 2%.
Based on basic rates, each region has the right to set its own territorial rates. The specified basic property tax rate can be reduced to zero or increased, but not more than three times. For example, the tax rate of 0.1% for residential properties in different regions varies from 0 to 0.3%.
You can find out property tax rates in your region on the Federal Tax Service website. For example, in 2018 in Moscow, regional tax rates coincided with the basic ones: for an apartment worth 8 million rubles they paid 0.1% of the cost, and for expensive property - from 300 million rubles - 2%.

How to calculate property tax for individuals
The amount per year depends on the rate and tax base. The rate is determined by law and regional authorities. The tax base is the cost of the object. It is multiplied by the tax rate and the amount of property tax is obtained.
Until 2014, the inventory value was used as the tax base. Inventory cost is an outdated calculation scheme that takes into account original cost and depreciation. The inventory value of the taxable object is not related to the market value. It was determined by the Bureau of Technical Inventory - BTI. The owner of the property can obtain a certificate of the amount of the inventory value. You need to contact the BTI at the location of the object.
Since 2015, to calculate property tax, they began to use the cadastral value - the price of the taxable object, calculated according to the Rosreestr scheme. This price is closer to the market price. Objects are assessed by employees authorized by Rosreestr.
You can find out the cadastral value of an object in four ways: in your personal account of Rosreestr, in your personal account of the Federal Tax Service, through a tax calculator on the tax website or on a public cadastral map. The inventory and cadastral value is also indicated in tax notices for the relevant years.



In most cases, the cadastral value is higher than the inventory value, so the amount of tax liabilities has increased. The difference can be three times or ten.
Let's take a real apartment in Omsk with an area of 60 m². The market value of this apartment is 2-3 million. According to the inventory, it cost 230,000 RUR, and according to the cadastre it costs 810,000 RUR - three and a half times more expensive.
In 2015, only 28 regions switched to calculating the cadastral value, the rest later. In 2019, eight regions still continue to calculate property tax at inventory value - these are the Altai Republic, Primorsky Territory, Irkutsk, Kurgan, Sverdlovsk regions, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, the Republic of Crimea and the city of Sevastopol.
Deductions for personal property tax
When calculating property tax based on cadastral value, tax deductions apply. A tax deduction is an area for which you do not have to pay. The larger the area of the taxable property, the greater its value. The deduction reduces the area of the property, the tax base decreases, so the total property tax amount becomes less.
Any home owner has the right to a tax deduction for each property he owns. It is taken into account automatically -
The tax deduction varies for different real estate properties: for a house - 50 m², for an apartment - 20 m², for a room - 10 m².
For a country house with an area of 100 m², the taxpayer will be charged half as much: only for 50 m² instead of 100. For a house with an area of 50 m² or less, no property tax will be charged at all.
The area of the Omsk apartment that we took as an example is 60 m². This means that you will only have to pay for 40 m².
Calculation based on cadastral value
To pay real estate taxes, you don't need to calculate anything first. The tax office will calculate everything itself, and the notification will already indicate the total amount for the reporting period. We'll tell you where it comes from so you can check it out. If it doesn’t work out, send a message to the Federal Tax Service.
Now there is a transition period for taxpayers: property taxes are not taken in full, but are multiplied by reduction factors. But first we will show how the full amount is calculated.
When calculating property tax based on the cadastral value, it is reduced by a deduction and multiplied by the tax rate. The tenure period is also important: if it is less than a year, the amount of property tax is proportionally reduced. If you own only part of the property, tax liabilities are divided proportionally between all owners.
N = B × S × KPV × D
Here N is the amount of property tax, B is the tax base, or the cadastral value of the object after deduction, C is the property tax rate in the region for this object, KPV is the coefficient of the ownership period, D is the size of the ownership share in the object.
To determine the CPV, you need to divide the period of ownership of the property in months by 12. If you bought an apartment before the 15th day inclusive, then this month is considered a full month. If later than this period, the month is not counted.
The taxpayer bought the apartment on June 20 and sold it on December 20. Then June is not taken into account in the period, but December is. Possession period - 6 months. CPV is 6/12, that is, 0.5.
You can also view the calculation formula in your personal account on the Federal Tax Service website. It will not necessarily coincide with ours, because we gave an example without taking into account reduction factors. To apply them, the organization first calculates property tax at inventory value. We will tell you how to do this further, but first we will calculate the full property tax according to the cadastre using a real example.
Calculation example
We will calculate the full amount of property tax according to the cadastral value for our apartment in Omsk for 2018. Its cadastral value is 810,000 RUR. Area - 60 m².
First, let's apply the tax deduction. To do this, let's calculate the cadastral value of one square meter: 810,000 / 60 = 13,500 RUR.
The area after deduction is 40 m², so the cost after deduction will be 13,500 × 40 = 540,000 RUR.
The tax rate for apartments in Omsk is 0.1%
If the taxpayer owned such an apartment for a full year, the CPV is equal to one. If he is the only owner, D is also a unit.
Full amount of property tax: 540,000 × 0.1% = 540 RUR.
If the taxpayer owned the apartment for only six months, the CPV will be 0.5.
Full amount of property tax: 540 × 0.5 = 270 RUR.
And if the taxpayer owns only a quarter of the apartment, D - 0.25.
Full amount of property tax: 540 x 0.25 = 135 RUR.
Calculation based on inventory value
Some regions still charge property taxes based on inventory value. In other regions, it is calculated in order to then be substituted into the formula for reducing property taxes based on cadastral value.
The tax office also calculates the amount based on the inventory value, but for clarity, we will describe how the total amount is obtained. The calculation formula is similar. Only the tax base is taken not from the cadastral value, but from the inventory value, multiplied by a deflator coefficient. The deflator coefficient is set by the government.
Tax deductions do not apply.
N = I × KD × S × KPV × D
Here N is the amount of property tax, I is the inventory value of the object, CD is the deflator coefficient, C is the property tax rate in the region for this object, KPV is the coefficient of the ownership period, D is the size of the ownership share in the object.
Calculation example
Let's calculate the property tax based on the inventory value for our Omsk apartment. The Omsk region switched to cadastre registration in 2016, so the last period for calculating the inventory value is 2015. Inventory cost - 230,000 RUR. The deflator coefficient in 2015 was 1.147.
On the Federal Tax Service website we find out the tax rate in Omsk for 2015. For apartments costing up to 300,000 RUR this is 0.1%.
Property tax based on inventory value: 230,000 × 1.147 × 0.1% = 264 RUR.
If the period of ownership of the apartment is six months, the specified amount will be halved and amount to 132 RUR.
If the taxpayer owns only a quarter of this apartment, he will pay 66 RUR.
The property tax at the inventory value turned out to be two times less than at the cadastral value. Therefore, when switching to a new calculation method, reducing factors apply.
Calculation based on cadastral value until 2020
Most owners do not yet pay the full amount of property tax at the cadastral value. To ensure a smooth transition to the new tax burden, reducing coefficients were introduced. 2020 is the deadline for the transition period to end for regions that began counting in a new way in 2015. From that time on, they were going to take taxes in full, but the conditions changed. Now, in most cases, the amount will be calculated taking into account reduction factors in 2020 and after it.
The amount of property tax is increasing gradually. In the first three years after the transition to the cadastre, the following formula is used:
Н = (Н1 − Н2) × К + Н2
Here N is the final amount of property tax for the current year.
N1 - the full amount of property tax according to the cadastre. We described above how it is considered.
N2 - tax liabilities based on inventory value for the last period when they were calculated. For example, in Moscow it is 2014, in the Omsk region - 2015.
K - reduction factor. In the first year after the transition to the cadastre, it is 0.2, in the second year - 0.4, in the third year - 0.6.
From the fourth year, the tax office compares the full amount of property tax at the cadastral value with the amount for the previous year. If the total amount has increased by more than 10%, the organization increases the amount of tax liabilities in the current period by 10%. If not more, from now on they take the full amount.
Full formula taking into account all parameters:
N = ((B x C - H2) x K + H2) x KPV x D - L
where L is a tax benefit.
When the amount according to the cadastral value is less than the property tax according to the inventory value, reducing factors do not apply.
Calculation example
Let's calculate how the property tax for our apartment in Omsk is growing. In 2015, it was taken according to inventory, and we paid 264 RUR. The full amount according to the cadastre is 540 RUR. Let's assume that the cadastral value will not change.
Growth in cadastral value for the first three years after the transition
| Year | Calculation | Total amount |
|---|---|---|
| 2016 | (540 − 264) × 0.2 + 264 | 319 R |
| 2017 | (540 − 264) × 0.4 + 264 | 374 R |
| 2018 | (540 − 264) × 0.6 + 264 | 430 R |
- 2016 - (540 − 264) × 0.2 + 264 = 319 R
- 2017 - (540 − 264) × 0.4 + 264 = 374 R
- 2018 - (540 − 264) × 0.6 + 264 = 430 R
Starting from 2019, we compare the total property tax with the amount for 2018. 540 R exceeds 430 R by more than 10%, so the real estate tax for 2019 will be 430 + (430 × 10%) = 473 R.
We are also comparing in 2020. 540 R exceeds 473 R by more than 10%, so the property tax for 2020 will be 473 + (473 × 10%) = 520 R.
We will compare again in 2021. 540 R exceeds 520 R by less than 10%, so we pay the full amount - 540 R. In 2022 and beyond, we will also pay this amount.
Benefits for individuals
Not everyone pays property taxes. Some categories are provided with benefits of 100 or 50%.
Tax benefits are provided only for property that is not used for business activities, for example, an apartment, room, house, garage. The benefit can be obtained only for one object of each type.
Grounds for providing tax benefits
Benefits are provided to certain categories of persons, for example, heroes of the USSR and the Russian Federation, disabled people of the first and second groups, participants of the Second World War, military personnel and their relatives, and pensioners. The list of preferential categories is specified in Art. 407 of the tax code. For them, property tax benefits are 100%.
These are federal benefits, and local governments in the regions add their own to them. You will find them on the Federal Tax Service website. Local benefits can be equal to the full amount of property tax or part of it.
Procedure for granting tax benefits
Benefits are provided upon application to the tax organization. An application for benefits must be submitted once at any time. It is possible even after calculating the property tax, then they will recalculate it retroactively. But it’s better before April 1 of the next year, then it will be taken into account in the calculation. For example, the deadline for submitting an application to reduce the amount of payments for 2019 is until April 1, 2020.
If you have several objects of the same type, indicate in your application what kind of benefit you want. You can change your choice at least every year, but you must do this before December 31 of the year for which you will pay. You don’t have to choose a preferential object at all, then the tax office will by default choose the object with the highest value.
If you own different types of real estate, tax breaks will be provided for each type. Since 2018, when submitting an application, you do not have to bring documents, but only provide details: the tax office itself will request the data and inform you of the decision.
The pensioner has two apartments: one in Moscow, with a cadastral value of 3 million, the other in Omsk, with a cadastral value of 810,000 RUR. Since the Moscow apartment is more expensive, by default he will receive a benefit for it. But according to the application, he can choose an Omsk apartment, then he will have to pay for the Moscow one. If we are talking about property tax for 2019, then the choice must be made before December 31, 2019.
This pensioner also has a private house. Since this is a different type of real estate, you won’t have to pay for it either.
He can submit an application for the benefit itself, and not for choosing an object for the benefit, at any time. If we are talking about property taxes for 2019, it is better to meet the deadline before April 1, 2020.
Do children pay property taxes?
If a child is the owner of an object or its share, real estate taxes must be paid for it. Disabled children are entitled to tax benefits. In some regions, orphans and minors in large families are also exempt from property taxes.
Property tax for individuals is calculated using the provisions of both federal and regional legislation of the Russian Federation. We will look at the main nuances of calculating the corresponding payment in our article.
Main elements of property tax for individuals
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, any tax is considered valid if the following elements are defined for it:
- an object;
- base;
- period;
- bid;
- procedure and terms of payment, as well as calculations.
In some cases, benefits may be established for certain taxes (clause 2 of article 17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Let us study in more detail the specifics of these elements.
Tax on real estate of individuals: objects of taxation
The corresponding object for the property tax of individuals may be (clause 1 of Article 401 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- separate residential building (including country houses);
- separate living space (in the form of an apartment or room);
- garage, parking space;
- building or structure for other purposes;
- unfinished construction;
- a complex of real estate objects of a single purpose.
The common real estate of an apartment building cannot be recognized as an object of taxation (clause 3 of Article 401 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax base for property tax for individuals
In the period from 2015 to 2019, the base for the tax in question is determined on the basis of the cadastral price of the objects we discussed above, if this is established by the legislative acts of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation. From 2020 - only on the basis of the cadastral price of the corresponding objects (clause 1 of Article 402 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If regional authorities have not adopted norms according to which the base is formed based on the cadastral price of real estate, then it is determined on the basis of the inventory value of objects, as long as this is permitted by law (clause 2 of Article 402 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Since 2015, based only on the cadastral value, the base for the objects mentioned in paragraph 1 of Art. 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if these objects are intended for use in business activities (clause 8 of Article 408, clause 3 of Article 402 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In general, the tax base for a particular property is equal to its cadastral value, except for those cases when the tax is paid (Article 403 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- per apartment - in this case, the cadastral base for it is reduced by the cadastral price of 20 sq. m in it (clause 3);
- room - in this case, the base for it is reduced by the cadastral price of 10 sq. m in it (clause 4);
- residential building - in this case, the base for it is reduced by the cadastral price of 50 square meters. m in it (clause 5);
- a single complex of real estate objects, including at least one residential premises or house - in this case, the base for it is reduced by 1,000,000 rubles. (clause 6).
Municipal legal acts may increase the amounts of the specified deductions that reduce the base for the tax in question (clause 7 of Article 403 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the use of a deduction leads to the formation of a negative value, the tax base will be equal to 0 (clause 8 of Article 403 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The base based on the inventory price is equal to the corresponding price multiplied by the deflator coefficient established by law.
Tax period and deadlines for payment of property tax for individuals
The tax period for the tax in question is a year (Article 405 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 409 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the real estate tax for individuals from 2016 (i.e., from the tax accrued for 2015) must be paid before December 1 of the year following the tax year. Tax is paid upon receipt of a tax notice from the Federal Tax Service. The payment must be transferred to the Federal Tax Service using the details of the Federal Tax Service division responsible for tax control of the territory in which the property is located.
Personal property tax: rates
To calculate tax based on cadastral and inventory values, different rates are applied. In both cases, they can be established by regional authorities - but within the limits reflected in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
According to the cadastral base, rates can be set at no more than (clause 2 of Article 406 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- 0.1%, if the object of taxation is a house, residential premises, unfinished construction, a single complex in which there is at least one residential premises or house, a garage, a parking space, a building in a country house with an area of up to 50 square meters. m;
- 2%, if the object of taxation is determined in accordance with the conditions of paragraphs. 7, 10 tbsp. 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation or has a cadastral value of more than 300,000,000 rubles;
- 0.5% - for any other objects.
Rates based on the cadastral base are accepted in the region in the amount specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, unless other rates are established by the law of the region (subclause 1, clause 6, Article 406 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, the region has the right to reduce (down to zero) or increase (but no more than 3 times) the rate for objects that, according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, are taxed at a rate of 0.1% (clause 3 of Article 406 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
According to the inventory base, rates can be set at no more than (clause 4 of Article 406 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- 0.1% if the inventory value of the object, taking into account the deflator coefficient, does not exceed 300,000 rubles;
- 0.1-0.3%, if the inventory value of the object, taking into account the deflator coefficient, is 300,000-500,000 rubles;
- 0.3-2%, if the inventory value of the object, taking into account the deflator coefficient, exceeds 500,000 rubles.
If the rates for the inventory base are not determined by the law of the region, then their value will be (subclause 2, clause 6, article 406 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- 0.1% if the inventory value of the object does not exceed 500,000 rubles;
- 0.3% if the inventory value is more than 500,000 rubles.
Regional authorities have the right to differentiate rates for both bases for objects of the same category, but different (clause 5 of Article 406 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- cadastral (inventory) value;
- type of object;
- location;
- specifics of the territorial zone in which they are located.
Procedure for calculating property tax for individuals
- cadastral and inventory price of the property;
- rates - cadastral and inventory;
- deflator value;
- object area;
- values of reduction coefficients;
- Are tax benefits applicable to tax calculation?
When calculating the tax from 2019, if for the region it turns out to be the 5th year of the beginning of the application of calculation from the cadastral value, it will not be necessary to take into account in the formula for its calculation:
- inventory value, as well as the rate that is set for it;
- deflator;
- reduction factor.
Property tax for individuals is calculated using a special formula established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For a full year of property ownership during 2015-2019, it looks like this (clause 8 of Article 408 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
H = (H1 - H2) × K + H2,
N - calculated property tax.
N1 - tax according to the cadastral base.
N2 - tax based on the inventory base, calculated for the year preceding the beginning of the introduction in the region of calculating the tax on the cadastral value. For 2014, it is determined according to the rules of the Law “On Taxes on Personal Property” dated December 9, 1991 No. 2003-I, which ceased to be in effect in 2015, and for later periods of the beginning of the introduction in the region of tax calculation based on cadastral value - according to the rules of the law region that was in effect in the year preceding the start of calculating the tax on the cadastral value.
K is a reduction coefficient, the value of which increases consistently during the first 4 years of the introduction in the region of calculating tax from the cadastral value, amounting to 0.2, respectively; 0.4; 0.6 and 0.8.
That is, from the 5th tax period (if calculations based on the cadastral value began in 2015, then it will be 2019), the tax will be charged on the cadastral value in full. Since tax calculation other than the cadastral value will be discontinued from 2020, regions that started doing it later than 2016 will not be able to use the right to apply reduction factors to the fullest extent.
We can consider how this formula is applied by studying a practical example of calculating the amount of tax.
An example of calculating the amount of property tax for individuals
- we started paying property taxes in 2015 and have the right to apply a reduction factor of 0.2;
- we do not have tax benefits (we will study their specifics a little later);
- we have an apartment of 70 sq. m;
- the cadastral price of the apartment is 2,000,000 rubles, the inventory price is 300,000 rubles;
- we live in Kazan, where there is a rate of 0.2% for the cadastral base (decision of the Kazan City Duma dated November 20, 2014 No. 3-38) and 0.1% for the inventory base at a cost of less than 500,000 rubles. taking into account the deflator (the norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are in force, the regional normative legal acts have not been adopted);
- the deflator coefficient established for the last year of application of the calculation from inventory value (2014) is equal to 1.216 (Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated November 7, 2013 No. 652).
The result of calculations is determined in whole rubles.
First of all, we consider the H1 indicator. For this:
1. Calculate the size of the cadastral tax base:
- divide 2,000,000 (real estate cost) by 70 (apartment area), we get 28,571 rubles;
- subtract from 70 sq. m "apartment" deduction in the amount of 20 sq. m, it turns out 50 sq. m;
- multiply the first result by the second, it turns out 1,428,550 rubles.
2. We determine the H1 indicator by multiplying the cadastral base by a rate of 0.2%. It turns out 2,857 rubles.
H2 = 300,000 × 1.216 × 0.1% = 365 rubles.
1. We subtract inventory N2 from the cadastral tax N1, it turns out 2,492 rubles.
2. We multiply the resulting result by the reduction factor established for the first year of application of the calculation in question, and we get 498 rubles.
3. Add inventory tax N2 to it, it turns out 863 rubles.
Thus, the real estate tax payable for 2015 will be 863 rubles.
We noted above that when calculating property taxes for individuals, benefits can be taken into account. Let's study this aspect in more detail.
For whom personal property tax is not mandatory?
In general, the payers of this tax are all individuals who own the objects we discussed at the beginning of the article. But some categories of citizens have property tax benefits. The list of these categories is fixed in the provisions of paragraph 1 of Art. 407 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If a citizen has the appropriate status, then he is exempt from paying property tax - but only for one object of taxation of each type (for example, 1 apartment, 1 house, 1 garage). If there are several objects of the same type, the person himself chooses which of them will not be subject to tax. By default, the Federal Tax Service, when calculating tax, selects the most expensive object from several for preferential treatment.
Results
The property tax for individuals during 2015-2019 can be determined both from the inventory value (if the region has not yet abandoned such a calculation) and from the cadastral value (if the decision to use such a base in the region has been made). From 2020, tax calculation will be possible only from the cadastral value. In the period from 2015 to 2019, provided that the region chooses to calculate from the cadastral value, a rather complex formula is used to determine the tax, taking into account the calculation from both the inventory and cadastral value.
Is a local tax, i.e. it is paid to the budget of the municipality (or the federal cities of Moscow, St. Petersburg and Sevastopol) in which it is installed and in which the property is located.
Who pays property taxes in 2018
Property tax must be paid by individuals who own:
- House;
- living space (apartment, room);
- garage, parking place;
- single real estate complex;
- unfinished construction project;
- other building, structure, structure, premises;
- share in the property listed above.
Houses and residential buildings located on land plots provided for personal subsidiary farming, dacha farming, vegetable gardening, horticulture, and individual housing construction are classified as residential buildings.
Note: for property that is part of the common property of an apartment building (staircases, elevators, attics, roofs, basements, etc.) there is no need to pay tax.
note that, according to the amendments made to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation by Law No. 401-FZ of November 30, 2016, non-residential buildings (garden and country houses) are equal to residential ones and are subject to property tax starting from the period of 2015. In relation to these objects, citizens can claim a benefit (if the tax is calculated based on cadastral value) in the amount of 50 sq.m. tax-free area. To obtain it, you must contact the tax authority in person or submit an application through the “Personal Taxpayer Account”.
How is property tax calculated for 2017?
Property tax is calculated by the Federal Tax Service, after which it sends a notification to the individual’s place of residence, which contains information about the amount of tax required to be paid.
On January 1, 2015, Chapter 32 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation came into force, which provides for a new procedure for calculating property tax. According to the new rules, the tax is calculated not from the inventory value of the object, but based on its cadastral value(i.e. as close as possible to the market).
The new calculation procedure will be introduced separately by each subject of the Russian Federation. Those entities that did not manage to approve the cadastral value of objects and publish the corresponding legal act before December 1, 2017, will calculate the tax in 2018 according to the “old” one (based on the inventory value).
Note: All subjects of Russia must completely switch to calculating property tax based on cadastral value by January 1, 2020.
How is tax calculated from cadastral value?
Property tax for individuals, based on the cadastral value of the property, is calculated using the following formula:
N to = (Cadastral value – Tax deduction) x Share size x Tax rate
Cadastral value
When calculating the tax, data on the cadastral value of an object is taken from the state real estate cadastre as of January 1 of each year (for new objects - at the time of their registration with the state). You can find out the cadastral value of an object at the territorial office of Rosreestr.
Tax deduction
When calculating tax, the cadastral value for the main types of objects can be reduced by a tax deduction:
The authorities of municipalities and cities of Moscow, St. Petersburg, and Sevastopol have the right to increase the amount of tax deductions described above. If the cadastral value turns out to be negative, then it is assumed to be zero.
Calculation example
Petrov I.A. owns an apartment with a total area of 50 sq. meters. Its cadastral value is 3,000,000 rubles. Cost of one sq. meter is equal to 60,000 rubles.
The tax deduction in this case will be: RUB 1,200,000(RUB 60,000 x 20 sq. meters). When calculating the tax, it is necessary to take the reduced cadastral value: RUB 1,800,000(RUB 3,000,000 – RUB 1,200,000).
Share size
If the object is in common shared ownership
Tax rate
Tax rates in each subject of Russia are different; you can find out their exact amount in 2018 on this page
| Tax rate | Object type |
|---|---|
| 0,1% | Residential buildings (including unfinished ones) and residential premises (apartments, rooms) |
| Unified real estate complexes, which include at least one residential premises (residential building) | |
| Garages and parking spaces | |
| Commercial buildings or structures whose area does not exceed 50 square meters. meters and which are located on land plots provided for personal subsidiary farming, dacha farming, vegetable gardening, horticulture or individual housing construction | |
| 2% | Administrative, business and shopping centers |
| Non-residential premises that are used to accommodate offices, retail facilities, catering facilities and consumer services | |
| Objects whose cadastral value exceeds 300 million rubles | |
| 0,5% | Other objects |
The authorities of municipalities and cities of Moscow, St. Petersburg, Sevastopol have the right to reduce the tax rate 0,1% to zero or increase it, but not more than three times. Also, depending on the cadastral value, type and location of the object, local authorities have the right to establish differentiated tax rates.
Calculation example
Object of taxation
Petrov I.A. belongs ½ apartments with a total area of 50 sq. meters. The cadastral value of the apartment is 3,000,000 rubles. The tax deduction will be equal to 1,200,000 rubles.
Tax calculation
To calculate the tax, we take the maximum possible tax rate 0,1% .
Substituting all the available data we get the formula:
900 rub.((RUB 3,000,000 - RUB 1,200,000) x ½ x 0.1%).
How is tax calculated on inventory value?
Property tax for individuals, based on the inventory value of the property, is calculated using the following formula:
N and = Inventory value x Share size x Tax rate
Inventory value
When calculating the tax, data on the inventory value submitted to the tax authorities before March 1, 2013 is taken. You can find out this information at the BTI branch at the location of the property.
Share size
If the object is in common shared ownership, the tax is calculated for each participant in proportion to his share in the ownership of this object. If the property is located in common joint property, the tax is calculated for each of the participants in joint ownership in equal shares.
Tax rate
Tax rates in each subject of the Russian Federation are different; you can find out their exact amount on this page. Please note that tax rates should not exceed the following limits:
Note: depending on the amount of inventory value, type and location of the object, local authorities have the right to establish differentiated tax rates.
Calculation example
Object of taxation
Petrov I.A. belongs ½ apartments in Moscow. The inventory value of the apartment is 200,000 rubles..
Tax calculation
The tax rate for this apartment is provided in the amount 0,1% .
The property tax in this case will be equal to: 100 rub.(RUB 200,000 x ½ x 0.1 / 100).
How is tax calculated under the new rules in the first 4 years?
When calculating the tax from the cadastral value, its amount is significantly larger than when calculating from the inventory value. In order to prevent a sharp increase in the tax burden, it was decided: in the first four years (after the introduction of new rules in the region), the tax should be calculated using the following formula:
Н = (Н к – Н и) x K + Н и
N to– tax calculated from the cadastral value of the object ().
N and– tax calculated from the inventory value of the object ().
TO– a reduction factor, thanks to which the tax burden will gradually increase by 20% each year.
Coefficient K is equal to:
- 0.2 – in the first year;
- 0.4 – in the second year;
- 0.6 – in the third year;
- 0.8 – in the fourth year.
Starting from the 5th year, property tax must be calculated based on the cadastral value of the property.
Note: tax calculation according to the above formula is carried out only in cases where the tax from the cadastral value is obtained more than from the inventory value.
Tax notice
For individuals, property tax is calculated by the tax service, after which it sends a tax notice to their place of residence, which contains information about the amount of tax, the deadline for its payment, etc.
Tax notices in 2018 will be sent to residents of Russia in the period from April to November, but no later than 30 days before the payment date.
Many real estate owners mistakenly believe that if they have not received a notice from the tax service, then they do not need to pay property tax. This is wrong.
On January 1, 2015, a law came into force according to which taxpayers in the event of non-receipt of tax notices are obliged self-report to the Federal Tax Service about the availability of real estate assets, as well as vehicles.
The above message, accompanied by copies of title documents, must be submitted to the Federal Tax Service in respect of each taxable object once before December 31 of the following year. For example, if an apartment was purchased in 2017, and no notifications were received regarding it, then information must be provided to the Federal Tax Service by December 31, 2018.
Therefore, if you do not receive a notification, the Federal Tax Service recommends taking the initiative and contacting the inspectorate in person (you can use this service to make an appointment online).
If a citizen independently reports that he has a vehicle for which tax has not been assessed, the payment will be calculated for the year in which the specified report was submitted. However, this condition only applies if the tax office did not have information about the reported object. If the payment notice was not sent for other reasons (for example, the taxpayer’s address was incorrectly indicated, or it was lost in the mail), then the calculation will be made for all three years.
For failure to submit such a message within the prescribed period, the citizen will be held accountable under clause 3 of Art. 129.1 and was fined in the amount of 20% of the unpaid tax amount for the object for which he did not submit a report.
Property tax payment deadline
In 2018, a single deadline for payment of property taxes was established for all regions of Russia - no later than December 1, 2018.
note that in case of violation of the deadlines for payment of property taxes, a penalty will be charged for the amount of arrears for each calendar day of delay in the amount of one three hundredth of the current refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. In addition, the tax authority may send a notice to the debtor’s employer to collect the debt at the expense of wages, and also impose a restriction on leaving the Russian Federation. There is no fine imposed on individuals for non-payment of taxes.
Payment of property tax
You can pay property tax using a special service on the official website of the tax service.
To do this you need:
How to find out your tax debt
You can find out if you have tax debts in several ways:
- By personally contacting the territorial tax authority of the Federal Tax Service at your place of residence.
- Through the taxpayer’s personal account on the official website of the Federal Tax Service.
- Using a special service on the Unified Portal of State Services.
- Through a data bank on the official website of bailiffs (only for debtors whose cases are in enforcement proceedings).
In 2019, there will be some innovations in the rules for paying property taxes. The procedure for calculating tax based on cadastral value will be adjusted and new grounds will appear on which it can be changed. The amount of tax on cadastral value will now increase annually by no more than 10%. Also, from the beginning of 2019, the tax on movable property will be abolished. We will talk about tax rates, benefits, reporting and penalties for property taxes in 2019.
How property tax changed in 2019
From January 1, 2019, changes to the property tax procedure will come into effect. Changes were introduced by Federal Law No. 302-FZ dated August 3, 2018:
- movable property is no longer subject to tax;
- Organizations submit tax reports for the quarter and year using a new form (Order of the Federal Tax Service dated October 4, 2018 No. ММВ-7-21/575@;
- Organizations submit tax reporting at the location of the property. The largest taxpayers still report to the tax office at their place of registration;
- the tax base is calculated separately for each property that is part of the Unified Gas Supply System.
To understand which property is classified as movable and which is not, read Article 130 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. All objects that are not classified as real estate are recognized as movable property, including money and securities. In addition, the Ministry of Finance draws attention to the fact that the property must be recorded in the Unified State Register or there must be grounds confirming the impossibility of moving the object.
Important! Property tax for 2018 must be paid on all movable property of 3-10 depreciation groups and registered after January 1, 2013.
Which properties pay property tax in 2019?
What property does an entrepreneur or organization pay tax on? The main feature of such property is its inclusion in fixed assets. This is stated in Art. 374 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The fixed asset must meet a number of conditions:
- they plan to use it in production, rent it out or use it for management purposes;
- it is planned to be used for more than a year;
- they do not plan to resell it for profit;
- the object can generate economic income.
Such property is transferred to accounting account 01 “Fixed Assets” and is subject to taxation, even if the object is in temporary or joint use. Companies also pay tax on residential premises that are not included in fixed assets (properties for sale).
The rules for paying property taxes have their own subtleties: if a fixed asset is used, its value is included in the tax base. This is done even if the facility has not yet been put into operation, has not been transferred to account 01, and the rights to the object have not been registered. If the fixed asset is not used and is not reflected in the account, then there is no need to pay tax (except for fixed assets that were received under a concession agreement).
Property that is listed in clause 4 of Art. is not subject to the tax. 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: land plots, cultural objects, icebreakers, spaceships and objects included in the first and second depreciation groups according to the OS Classifier. Enterprises on the simplified tax system and UTII pay tax only on real estate - these are objects from the cadastral list of regions.
Benefits when paying property taxes in 2019
For some types of property, benefits are applied that exempt the organization from paying tax (see):
- if your organization is part of a free economic zone, belongs to the religious sphere or the penal system;
- property of Skolkovo residents, prosthetic and orthopedic enterprises, advocacy and legal consultations, state research centers;
- no longer need to pay movable property tax.
Regions can establish their own benefits, reduce rates and exempt from paying taxes, so check the information on benefits and rates in your region on the official website of the tax service.
How to calculate property tax in 2019
The tax service calculates the tax for entrepreneurs and sends them a notice for payment. Organizations must calculate the tax themselves. In an accounting web service you can do this automatically.
- First you need to figure out which of your existing assets is subject to tax.
- Next, you should check whether the organization is entitled to benefits - data on benefits is contained in regional laws.
- Find out the basis for calculating tax.
- Find out the tax rates established in the region.
- Calculate the tax payable to the budget.
Advance tax payments are made quarterly. Calculation for the quarter is carried out according to the following formulas:
Property tax at average annual value = Average cost of fixed assets for the reporting period x Tax rate / 4
Property tax by cadastral value = Cadastral value of property x Tax rate / 4
Separate divisions pay tax at the rate of the region where the division is registered. If the property is not located at the place of registration of the parent organization or division, then the tax is calculated at the rate of the region where the property is located.
Example of calculating property tax based on average annual value
The tax base is calculated by adding the residual value of each object on the first day of each month and on the last day of the billing period. The tax base of depreciated objects is zero, but the objects are included in the report.
Residual value of fixed asset:
- January 1 - 150,000 rubles
- February 1 - 145,000 rubles
- March 1 — 140,000 rubles
- April 1 — 135,000 rubles
- May 1 - 130,000 rubles
- June 1 - 125,000 rubles
- July 1 - 120,000 rubles
- August 1 - 115,000 rubles
- September 1 - 110,000 rubles
- October 1 — 105,000 rubles
- November 1 - 100,000 rubles
- December 1 — 95,000 rubles
- December 31 — 90,000 rubles
Advance payment for 1st quarter
Tax base = (150,000 + 145,000 + 140,000 + 135,000) / 4 = 142,500 rubles
Payment = 142,500 * 2.2% / 4 = 783.75 rublesAdvance payment for half a year
Tax base = (150,000 + … +125,000 + 120,000) / 7 = 135,000 rubles
Payment = 135,000 * 2.2% / 4 = 742.5 rublesAdvance payment for 9 months
Tax base = (150,000 + … + 105,000) / 10 = 127,500 rubles
Payment = 127,500 * 2.2% / 4 = 701.25 rublesAdditional tax payment for the year
Tax base = (150,000 + … + 90,000) / 13 = 120,000 rubles
Payment = 120,000 * 2.2% - (783.75 + 742.5 + 701.25) = 412.5 rubles
If you pay property tax based on cadastral value
From 2019, all of Russia will calculate tax from the cadastral value. Authorities must warn companies and publish a list of properties to pay tax at cadastral value. The publication is made before January 1 on the official website of the region. If there is no such publication or your property is not listed, then continue to pay tax at the average annual value.
Request the cadastral value of the building from the regional office of Rosreestr. If you own only part of the building, then find out its cadastral value based on your share of the total area of the building. The tax amount is determined using the following formula:
Tax amount for the year = cadastral value * tax rate * number of months of property ownership / number of months in the reporting period
If your region provides advance payments, then the quarterly payment is equal to a quarter of the tax amount. It happens that in the middle of the year the authorities exclude an object from the list of property for payment of tax at the cadastral value, then the tax will have to be recalculated from the beginning of the year at the average annual value.
Since the change in the procedure for calculating tax from inventory valuation to cadastral value, disputes have arisen between taxpayers and cadastral authorities. Revaluation is carried out no more than once every 3 years, so it is important to be able to appeal the commission’s decision. The reason for changing the rating may be:
- incorrect indication in the list of real estate objects;
- incorrect definition of conditions affecting the value of real estate;
- incorrect application of data when calculating cadastral value;
- failure to use information about the emergency condition of the facility.
Legal entities can appeal the assessment only through the cadastral dispute commission. To appeal, you must provide the commission with documents confirming the errors made during the assessment.
Changes in cadastral value that appear after January 1, 2019, apply from an earlier period. They are taken into account when calculating the tax base from the date of commencement of application of the changed or disputed cadastral value.
Reporting on property tax of organizations
Quarterly calculations are submitted for advance payments, and a property tax declaration is submitted at the end of the year. Since 2019, the forms of calculation and declaration have been changing; they were approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service dated October 4, 2018 No. ММВ-7-21/575@. The new forms take into account the cessation of taxation of movable property, and they also allow tax to be calculated if the cadastral value was changed during the tax period. The declaration now includes the field “Address of the real estate property” for objects that do not have a cadastral number, but do have an address.
The property tax return for 2018 is due by April 1, 2019, subject to postponement. Calculations are submitted within 30 days after the end of the reporting quarter:
- calculation for the 1st quarter of 2019 - until April 30, 2019;
- calculation for the half year 2019 - until July 30, 2019;
- calculation for 9 months of 2019 - until October 30, 2019.
Many regions introduce their own deadlines for reporting and paying taxes - and approach this issue in a varied and creative way. You need to clarify the conditions and reporting dates of your region. Payment of advance payments or taxes is made at the location of the property. In the same way, property reports are submitted to the tax office at the location of the property. The fine for companies that fail to notify the tax authorities about real estate is 20% of the unpaid property tax.
Try to easily and quickly prepare property tax calculations in the Kontur.Accounting online service. At the end of the year, generate and send through Kontur.Accounting a property tax report and other tax returns and reports to funds.